|
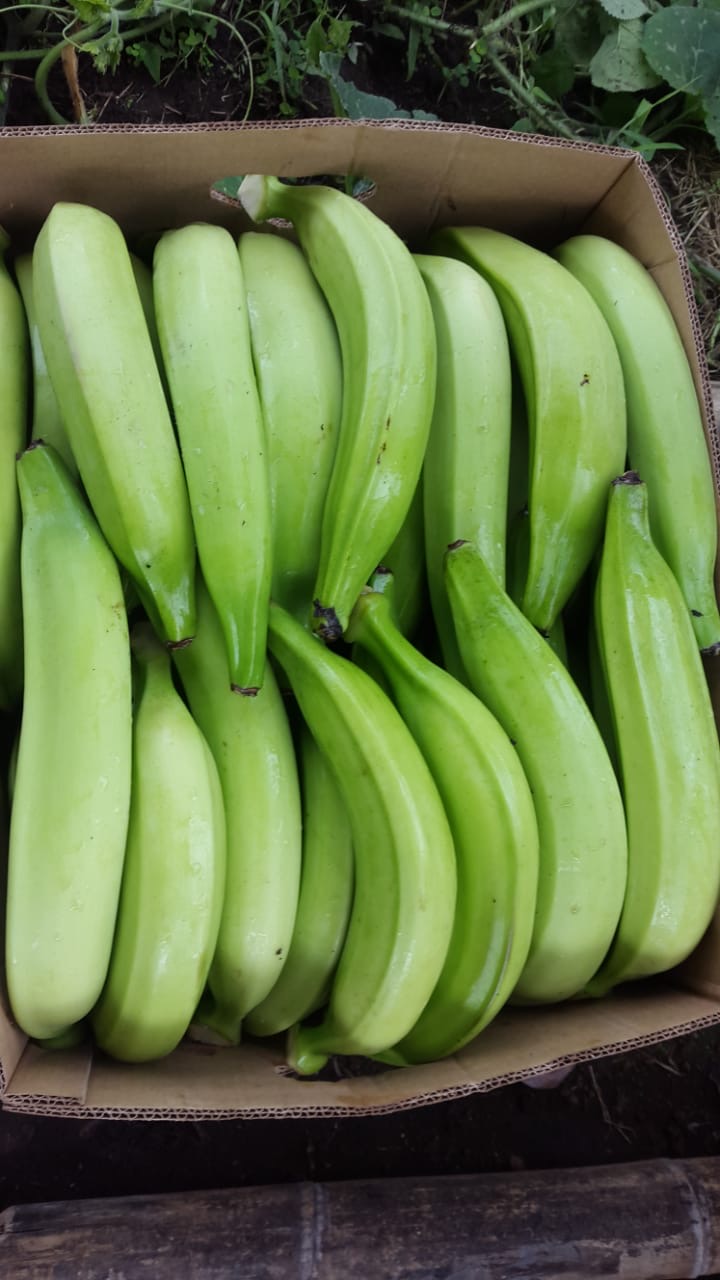
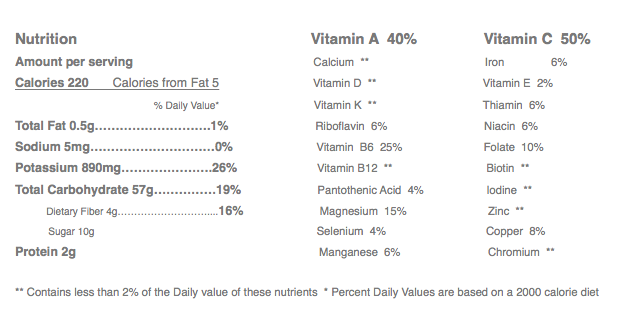
Many people confuse plantains with bananas. Although they look a lot like green bananas and are a close relative, plantains are very different they are longer than bananas and they have thicker skins. They are starchy, not sweet, and they are used as a vegetable in many recipes, especially in Latin America and Africa. Plantains are sold year round in the fresh produce section of the supermarket. Variety: Barraganete-Macho Availability: January to December Packaging: 60-70 units per box (22.70 Kilos per box). 1 CONTAINER = 1,080 boxes = 20 pallets with 54 boxes per pallet Nutrition Facts Click the image below to see nutrition facts. To contact us about plantains, click here. |
Health benefits of Plantains
Plantain relatively has more calories weight for weight than that in the table bananas. 100 g plantain holds about 122 calories, while dessert banana has only 89 calories. Indeed, they are very reliable sources of starch and energy; ensuring food security for millions of inhabitants worldwide. It contains 2.3 g of dietary fiber per 100 g (6% of DRA per 100 g). The adequate amount of dietary fiber in the food helps regular bowel movements, thereby reducing constipation problems. Fresh plátanos have more vitamin-C than bananas. 100 g provide 18.4 mg or 31% of daily required levels of this vitamin. Consumption of foods rich in vitamin-C helps the body develop resistance against infectious agents and scavenge harmful oxygen-free radicals. However, boiling and cooking destroy much of this vitamin in plantains. Plantains carry more vitamin A than bananas. 100 g fresh ripe plantains contain 1127 IU or 37.5% of daily required levels of this vitamin. Besides being a powerful antioxidant, vitamin-A plays a vital role in the visual cycle, maintaining healthy mucosa, and enhancing skin complexion. As in bananas, they too are rich sources of B-complex vitamins, particularly high in vitamin-B6(pyridoxine). Pyridoxine is an important B-complex vitamin that has a beneficial role in the treatment of neuritis, anemia, and to decrease homocysteine (one of the causative factors for coronary artery disease (CHD) and stroke episodes) levels in the body. Also, the fruit contains moderate levels of folates, niacin, riboflavin and thiamin. They also provide adequate levels of minerals such as iron, magnesium, and phosphorous. Magnesium is essential for bone strengthening and has a cardiac-protective role as well. Fresh plantains have more potassium than bananas. 100 g fruit provides 499 mg of potassium (358 mg per 100 g for bananas). Potassium is an important component of cell and body fluids that helps control heart rate and blood pressure, countering adverse effects of sodium. |
|